DEVELOPMENT OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY IN ANCIENT INDIA
Good knowledge of measurement and geometry is shown in the town planning of Harappa. The Sulvasutras are supposed to be the origination of Indian mathematics. Apastamba introduced practical geometry in the second century B.C. which involves acute, obtuse and right angles. This knowledge was of great help in the construction of fine altars wherein the kings offered sacrifices.
From the Indus valley excavation points, bronze and copper artefacts and glazed potteries are found which shows their knowledge of highly developed metallurgy. The Vedic people were also aware of the process of fermenting grains and fruits, tanning leather as well as dyeing.
The first century A.D. also witnessed mass production of metals such as iron, copper, silver, and gold and also of alloys such as bronze and brass. Textile dyeing was also very popular during that time. Indian contribution to shipbuilding reflects in Lothal, a site in Gujarat which has the remains of a dockyard providing evidence that trade flourished in those days by sea.
Varahamihira was among the nine gems in the court of Vikramaditya. The king gave him the title of ‘Varaha’because of his accurate predictions. His Brihat-Samhita is considered a pioneer work in the field of astronomy. He observed that the moon rotated around the earth and similarly the earth rotated around the sun. Baudhayan was the first person to calculate the value of the pie. Pythagoras theorem is found in Baudhayan’s Sulva Sutra.
Also, See once…
Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Geography
The summary of mathematics was mentioned in the book of Aryabhatta known as Aryabhatiya. He explained zero as a symbol as well as a concept which helped him in understanding the exact distance between that the earth and the moon. He also mentioned that earth is round and rotates on its own axis. He also correctly stated that reflected sunlight is the reason behind the lustre of the moon and the planets.

In his book Aryabhatiya, he described the movement of the sun and the moon and also the calculation of the eclipses. Aryabhatta explained that the rationale behind this explanation was the shape of the earth and its rotation on its own axis. At times when the earth’s shadow falls on the moon, it caused a lunar eclipse and similarly, when the shadow of the moon fell on the earth, it caused a solar eclipse.
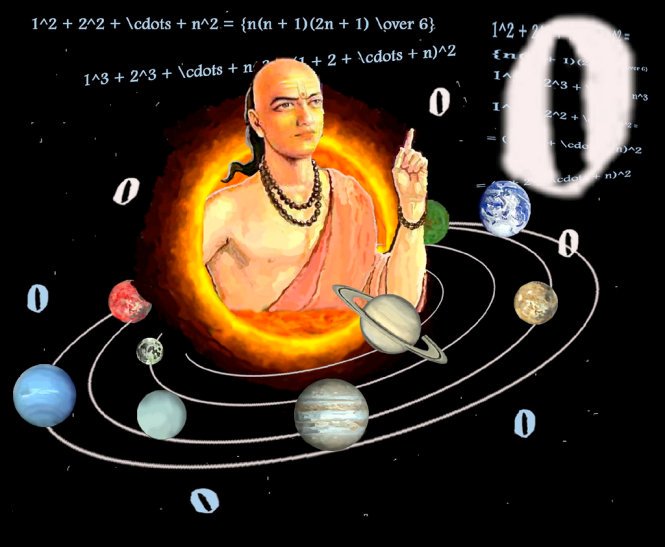
Brahmgupta, introduced multiplication methods in which he used place value in almost the same way as it is used today. In his famous work Brahma Sputa Siddantika, he introduced negative numbers and operations on zero. Bhaskaracharya is famous for his book Siddhanta Slummani, which is divided into four sections: Lilavati (Arithmetic), Beejaganit (Algebra), Goladhyaya (Sphere) and Giahaganit (mathematics of planets). He also introduced a method to solve algebraic equations called as Chakrawat Method or the Cyclic Method. The first textbook on arithmetic written in present-day form is that of Ganit Sara Sangraha which was written by Mahaviracharya in 850 A.D. He is also the one who introduced the current method of solving the least common Multiple (LCM) of given numbers.
Kanad, a sixth-century scientist propounded an atomic theory which is very much similar to the modern-day atomic theory. According to him, a material universe which is made up of kanas is invisible and indestructible. Varahamihira played an important role in the fields of geology, hydrology and ecology. He had also stated that the presence of termites and plants could very well be indicators of the presence of underground water. In his book Brihat Samhita he tried to co-relate the natural process such as undersea activities, planetary motion and unusual cloud formation as causes of earthquakes. A scientist named Nagarjuna in the tenth century tried to convert base elements into gold. Unfortunately, he did not succeed but was able to make an element of gold-like shine and now this very same technology is administered for the making of imitation Jewellery. He also discussed the methods for the extraction of many metals including gold, silver and copper, etc. in his book Rasaratnakara.
Also, See once…
Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Geography
Ayurveda is the oldest branch of medical science which was developed in ancient times on our Planet. The oldest known medical book in the world is Atreya Samhita. Charak is known as the father of ayurvedic medicine and Susruta is known as the father of surgery. Susruta, Charak, Vagbhatta, Madhava and Jeevakare are a few renowned names that belong to Ayurveda. In Atharva Veda for the first time diseases, their cure and medicines were mentioned, e.g., fever, cough, consumption, diarrhoea, dropsy, sores, leprosy, etc. In India, places such as Takshila and Varanasi emerged as centres of medicine and learning. Charak Samhita by Charak and Sushrut Samhita by Sushruta are the two important texts in this field. In the court of Kanishka, Charak was the Raj Vaidya (royal doctor). He is credited as the first person who talks about digestion, metabolism and immunity. He also knew the concepts of Genetics.

In Charaksamhita, the use of plants and herbs for medical purposes was also mentioned. Sushruta, the pioneer surgeon in Indian history studied human anatomy with the help of a dead body. In his book Sushruta Samhita, he described the method of selecting and preserving a dead body for the purpose of its detailed study. His book mentioned about 1,100 diseases including different types of fever, jaundice and urinary complaints. He greatly contributed to Rhinoplasty (plastic surgery) and as well as in ophthalmic surgery (removal of cataracts). Surprisingly, modern surgeons use techniques similar to that of Shusruta during plastic surgeries. He has mentioned 121 surgical instruments along with mentioning the methods of operations, bone setting and cataract, etc. Sushruta also mentioned that 760 plants have medicinal value.
Yoga originated in ancient times as an allied science of Ayurveda for healing without medicine at the physical and mental levels. The term Yoga is derived from the Sanskrit word Yoktra (yoking of the mind to the inner self after detaching it from the outer subjects of senses). Hath yoga is physical and mental yoga, whereas Raja yoga is mental yoga. The purpose of yoga is self-realisation and liberation from bondage by achieving physical, mental, emotional and spiritual balance. Patanjali is the person behind this great science. In his book Yoga Sutras, he mentioned ‘Aum’as a cosmic sound spoken of as the symbol of God. Among his other works, Patanjali is known for his book on medicine and his work on Panini’s grammar, known as Mahabharata.
Also, See once…
Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Geography
Please write your feedback in the comment section.
Related Links, Visit Once
History of Gautama Buddha
History of First World War
History of Second World War
10 Better GOOGLE MAP’S Alternative
How Science and Technology Affecting Human Life
Development of Science and Technology in Medieval India
